What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is identical or similar content that appears on multiple URLs within the same (internal) or across different websites (external). It confuses search engines and affects user experience, resulting in lower visibility and ranking in SERPs.
In simple terms, Search engines might think you’re trying to trick them by posting the same content repeatedly for more traffic from one single content.
Types of Duplicate Content
- Exact Duplicate Content: The same content word-to-word on many websites. Example: Copied, Distributed, or Scraped
- Near-Duplicate Content: Similar content with minor changes in wording or formatting.
- Content Syndication: When you publish your content on multiple websites with proper authorization but without canonicalization.
Reasons Why you Should Fix Duplicate Content
One SEO-optimized indexed article is better than duplicate issues that Google crawls but does not indexed. It not only affects indexing but also confuses Users and Search Engine crawlers.

- Confuses Search Engine: Having multiple pages on same topics can confuse search engines which page to rank.
- Crawling Inefficiency: You will waste your “Crawl Budget” on duplicate pages instead of focusing on unique, important content, resulting in the inability to discover and index new content.
- Ranking Dilution: Multiple versions will compete against each other for the exact keywords. Resulting in lower overall search engine rankings.
- Backlink Split: Backlinks will split between duplicate pages, weakening overall link equity and authority which can negatively impacting your SERP ranking.
- Potential Penalties: Google wants to provide the best User Experience and if you are constantly delivering similar content. Then the chances of penalty increases.
- Poor User Experience: If the user visits duplicate content instead of the preferred version, it can lead to a negative experience, resulting in higher bounce rates, lower engagement, and decreased conversions.
What Causes of Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content issues can be caused by various reasons, including the content itself, URL, and technical issues.
URL Variations:
One of the reasons for duplication is if your URL is not properly configured.
- WWW vs non-WWW: Select a preferred version and redirect other to primary domain.
- HTTP vs HTTPS: Use HTTPs for secure websites and make proper redirection from non-secure versions.
- Parameter-based URLs: URLs with tracking or sorting parameters result in multiple versions of the same content.
- Session IDs: Dynamic URLs containing session IDs create duplicate content.
Content Duplication Across Pages:
- Pagination: Poor pagination management for archives pages, long articles, or comments.
- Sorting and filtering options: The E-commerce site’s filtering and sorting features may generate duplicate URLs.
- Tag and Category pages: CMS platforms (like WordPress) create duplicate archives for tags and categories.
- Printer-friendly pages: Separate URLs for standard and printer-friendly versions.
- Boilerplate content: Repeating the exact text (e.g., legal disclaimers) across many pages.
- Duplicate meta tags: Same title tags and meta descriptions across multiple pages signal duplication.
Copied or Scraped Content:
You should always check for plagiarism after you finish writing your article. It might not be intentionally but ideas and can match with existing articles, which can cause duplication.
Another scenario: Let’s say you have a perfect SEO-optimized blog post that ranks for the primary keyword, but then you see a drop in traffic and ranking. Then you find out someone copied your content.
It does not matter if you Copy/Paste or if someone else scrapes your content. Google decides which one will get the priority based on its algorithm and authority of the website.
You can complain to Google if someone has copied your content.
Multi-language:
For websites with different languages without proper hreflang tags, search engines treat them as duplicates.
How to Identify Duplicate Content? [Free and Paid Tools]

You will need basic a knowledge on how to use these SEO tools other way is to ask for help from an SEO expert or community to identifying and solve your issue.
To identify, you can either check manually or use tools. Free tools and paid both works; the only difference is that paid is in-depth, provide more information to save time and are recommended to crawl for big sites.
Free Methods
- Search Console: Check if your Website has a Duplicate Content Issue on the console. It is free and provides an accurate report.
- Screaming Frog [Free Version]: Recommended for small sites only as it crawls up to 500 URLs for duplicate meta tags and content. [Recommended]
- Siteliner: It scans your site for internal duplicate content and reports for free. [Limited]
- Google Search: Using “Google Search” and “Operator” manually is a free process to check for duplicate content, but it is time-consuming. (Internal and External)
- Other: Use Plagiarism checkers or Grammarly (Free Version) to check for small amounts of content for duplication.
Paid Methods
- Screaming Frog (Paid Version): Crawl unlimited URLs and find duplicates. [Recommended for Large Websites]
- Copyscape: One of the most popular tools for checking external duplicate content. (Pay-per-use for full scans)
- Ahrefs: Provides a “Site Audit” tool that detects internal and external duplicate content. [Best All-in-One SEO Tool]
- Semrush: Offers a comprehensive site audit for finding duplicate content across your Website. [Affordable All-in-One SEO Tool]
- Moz Pro: Includes a duplicate content checker within its SEO suite.
How to Fix Duplicate Content?
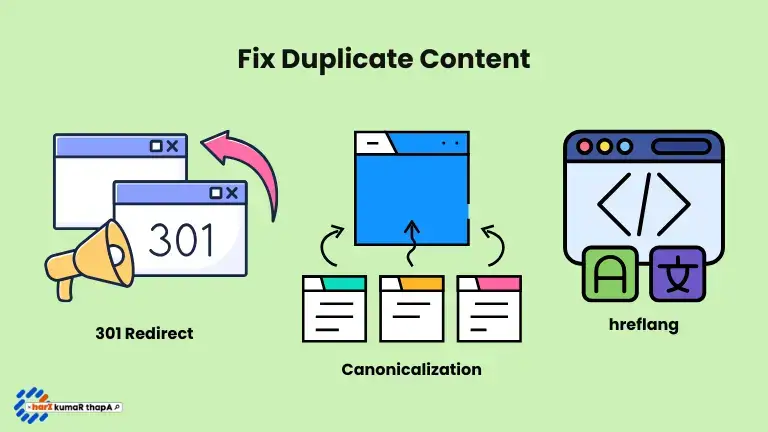
301 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a commonly used technique in SEO to solve duplicate content issues. It redirects bots, users, and page authority to a new page.
Redirect duplicate URLs to the preferred version of the page. Plugin like Rank Math has a redirection feature.
To avoid duplicate versions, you can set your preferred domain in Google Search Console (www or non-www).
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are a way to tell search bots there are multiple versions of this page. It helps crawl bots to understand which page is to Crawl, Index and Rank.
Use the <link rel=”canonical”> tag to set the preferred version for a page.
Plugins like Rank Math or Yoast SEO will insert Canonical tags automatically. It help determine preferred version for:
- Pagination,
- Syndicated Content,
- HTTP vs HTTPS or www vs non-www Versions,
- Similar content across multiple URLs,
- Duplicate Pages from Sorting or Filtering (e-commerce).
Use hreflang:
The hreflang tag signals to search engines which language or regional version of your content to display, ensuring similar pages in different languages or regions aren’t treated as duplicates.
Content Consolidation
Merge similar or duplicate pages into one comprehensive page. And set up redirects from the old pages.
Example: If you have a similar article on a topic, you can merge them into one article.
- “How to Brew the Perfect Cup of Coffee at Home”
- “Best Brewing Techniques for a Great Coffee Experience”
Result: “The Complete Guide to Brewing the Perfect Cup of Coffee at Home”
Meta Tags Optimization
Write unique title tags and meta descriptions to avoid duplicate content.
Also, WordPress automatically creates Category and Tag pages, which can cause duplicate issues.
Block Duplicate Pages through Robots.txt
Update the Robots.txt file to block search engines from crawling and indexing. It will help avoid duplicate content issues.
Get Expert Help
Struggling to find a fix for duplication issue on your own? Rather then making a mess and regretting it later consult an SEO expert with experienced hands-on expertise to identify the root cause and apply the right solutions.
Whether it’s technical issues or content overlap, professionals can deal with it to keep site optimized and error-free.